Lab Seminar - Optimal spatial allocation of different types of treatment for COVID-19
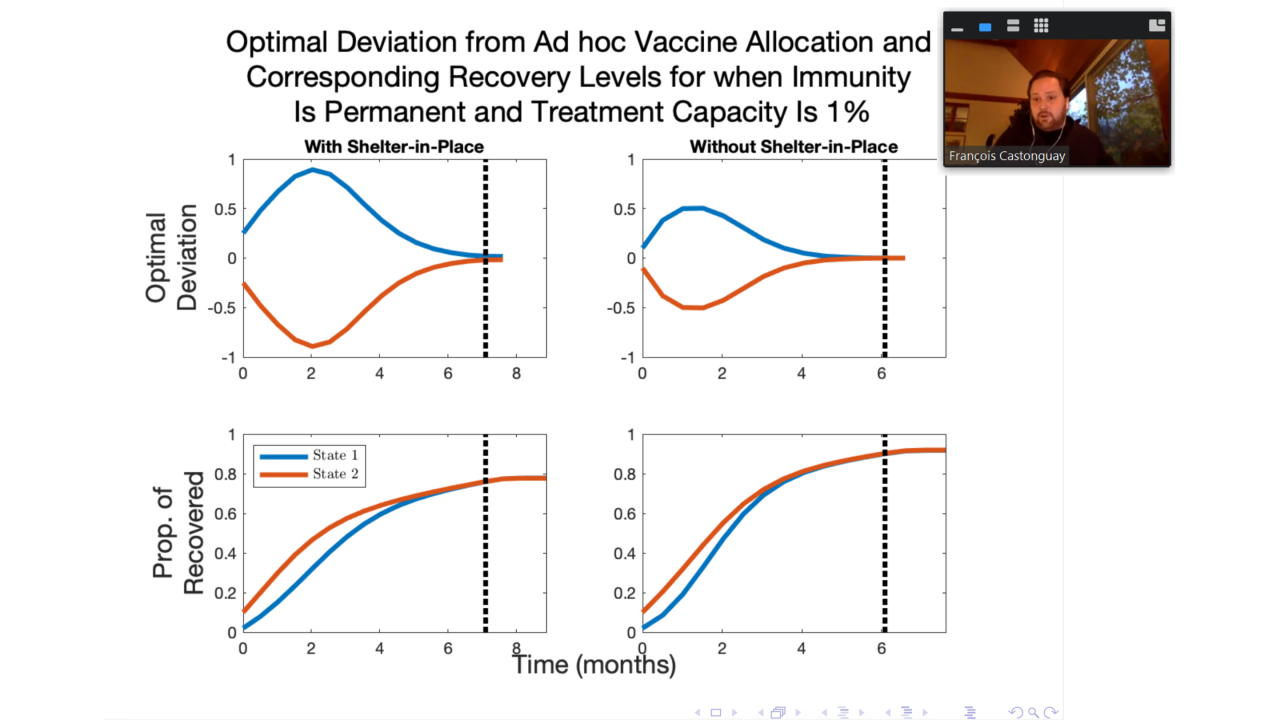
François Castonguay updated his research on optimal allocation of treatment for COVID-19. While clinical trials are under way to find an effective treatment for coronavirus (COVID-19), inherent differences across jurisdictions has made the disease burden highly heterogeneous across space. Yet, recent recommendations by the U.S. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine suggest that a fair allocation of treatment should be based on population size. By combining epidemiological modeling with tools from economics and mathematics, we investigate the benefits and costs of deviating from an allocation based on population size when supplies of effective drugs and vaccines are limited in supply. Using optimal control techniques, we solve for allocation rules for a vaccine and for a drug treatment that minimize the economic damages related to infectious individuals and deaths, expenditures related to treatment, and a penalty cost representing the social costs of deviating from a fair allocation. We consider different scenarios where the length of immunity, the compliance to a shelter-in-place order, and the treatment capacity is varied. We find that it is always optimal to deviate from the relative population allocation rule. Because drugs and vaccines attack different points in the disease pathology, the benefits from deviating depend on treatment type. For drug treatment, extreme cases where all the allotment is given to one state for a period of time is the norm rather than the exception. For vaccines, the benefits from deviating are especially high when immunity is permanent, when there is compliance to a shelter-in-place order, and when treatment capacity is low. Interestingly, a lack of compliance to a shelter-in-place order pushes the optimal allocations of vaccine towards the fair allocation, as the mixing of the populations reduces some of the structural heterogeneity in disease burden.